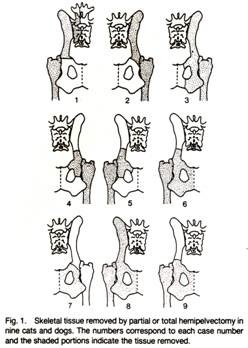
+ General Considerations
- OSA and CSA are the most common pelvic tumors
- pelvis OSA had a similar biologic behaviour to appendicular OSA
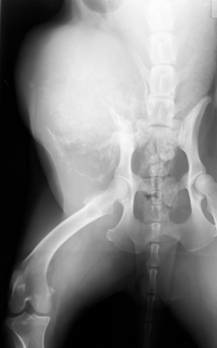
- diagnosis: survey radiographs and CT to assess presence and degree of sacral involvement
+ Treatment
- 3 classifications of hemipelvectomy: radical, conservative, and internal
- Radical: limb amputation with separation of pelvis through sacroiliac joint
- Conservative: limb amputation with preservation of sacroiliac joint and cranial ilium
- Internal: preservation of limb
- Musculocutaneous flaps are preferred for wound closure although fasciocutaneous flaps acceptable
- Medial extent of the tumor is the most difficult dissection with midline (sacrum or pubis) the surgical limit
- Complications are rare and similar to limb amputation
- Complications in humans include infection, skin flap necrosis, herniation, fecal and urinary incontinence if pudendal nerve roots transected, thromboembolic disease, and local tumor recurrence